There are many foods that share strong similarities with other foods, and one great example of this is the pairing of yams and sweet potatoes. These two starchy root veggies often spark bundles of confusion regarding which is which—but no longer! Here’s a quick guide regarding the main differences between yams and sweet potatoes.
Settling the Score
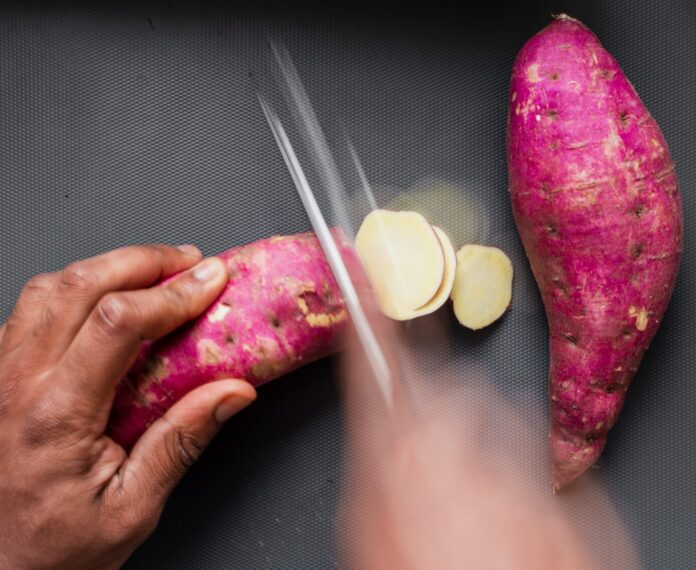
First things first, let’s clear up the misconception: what you typically find in your local grocery store labeled as “yams” are actually sweet potatoes. In fact, true yams are not commonly found in most Western markets. When you think of yams, picture a tropical tuber with rough skin and a starchy interior, quite distinct from the sweet potato’s orange flesh.
Sweet Potatoes Are More Diverse Than You Think
Sweet potatoes come in various colors ranging from orange and yellow to white and even purple. Each variety boasts its unique flavor profile, sweetness, and texture. So, whether you prefer a sweeter and moister sweet potato or a drier and starchier one, there’s a sweet potato out there to suit your taste buds.
Different Origin Stories
Another key difference lies in the geographical origins. Yams are primarily found in Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean, whereas sweet potatoes have their roots in Central and South America. However, due to historical reasons, the term “yam” is often used interchangeably with sweet potatoes in certain regions, leading to confusion.