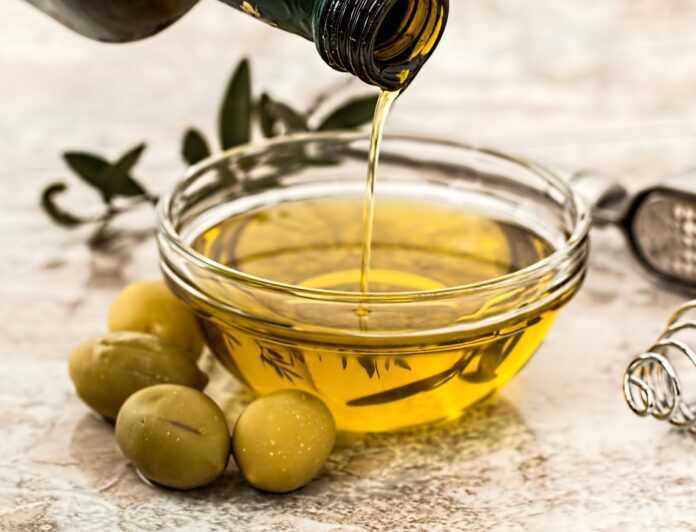
Olive oil is a kitchen staple prized around the world for its flavor and versatility, used to add richness to a wide range of recipes from salad dressings to desserts. Obviously, all types of olive oil are made from olives, but that doesn’t mean they’re all created equal. There are many types of olive oil on the market, and it’s important to understand the differences between them in order to choose the right kind for your recipe. Read on for a quick guide.
Virgin Olive Oil
Like its extra-virgin counterpart, virgin olive oil is derived from the first cold pressing of olives, but has a slightly higher acidity level and a milder flavor. While the quality of olives used to produce this type of oil is generally still good, it typically involves a broader range than what’s used to create extra-virgin olive oil. Use it in baked goods to add a subtle fruity flavor, over drizzle it over veggies when grilling or sautéing.
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil
As the highest quality olive oil, EVOO is extracted from the first press of freshly picked olives and undergoes minimal processing without chemicals or heat. The result is a robust, heart-healthy oil high in antioxidants and unsaturated fats. Its bold flavor and low acidity make extra-virgin olive oil the best choice for salads and other raw dishes, though it also makes a great finishing touch over soups.
Pure Olive Oil
Don’t let the name fool you—pure olive oil may sound totally natural, but it actually includes a blend of virgin and refined oils, the latter of which is processed using extensive heat and filtration. This type of oil is well-suited to cooking methods like grilling and frying, where its neutral flavor and high smoke point can prevent sticking without affecting taste.